No idea how much Protein to eat? Know your Daily Protein Intake
There exists a sense of muddle among the fitness world. Everyone talks about the importance of protein in your diet. But when you narrow it down to how much protein is daily required, everyone has a different advice for you. Some people will tell you to eat a lot of protein to get a good and a healthy body.
There are then some others who will warn you against the harmful effects of eating too much protein. So, how much protein is too much protein for you? How much protein is required to complete your daily protein intake?
If these are some questions bobbing your head, then this article will be a perfect fit for you. This article will answer all your questions related to the daily protein intake and the amount of protein you should eat daily. Also, you will get to know if eating too much protein can pose any possible dangers to your health or it’s just another debunked theory.
Why to eat Protein in your Diet?
Protein is an important macronutrient in your diet. It has an active role in building and repairing the tissues of your body. You need to have protein to build your bones, cartilage and muscles. Your body needs protein in good amounts like the other two macronutrients namely the carbohydrates and the fats. These three macronutrients are vital for body to function efficiently and produce energy.
All these three macronutrients contains three elements namely carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. However, it is the protein which contains extra element nitrogen linked to it. The Nitrogen is a necessity of human body which is responsible for producing amino acids in the body [1].
The amino acids are the building blocks of protein which are required to perform the metabolic processes in your body. These amino acids are responsible for production of hormones, enzymes and other chemicals which are important for carrying out the life processes of your body.
There are 20 amino acids which are responsible for body`s metabolic processes. Out of 20 amino acids, 11 amino acids are produced in enough amounts by your body and hence known as non essential amino acids.
The remaining 9 amino acids can`t be produced by your body and hence you need to obtain them through your diet. These types of amino acids are known as essential amino acids. In order to have these essential amino acids present in your body, you need to have variety of protein foods in your diet.
How much Daily Protein Intake is recommended?
The daily protein needs are variable and varies for different individuals. How much protein you eat depends upon your current health, fitness and activity level. Well, if you need a precise answer on daily recommended protein intake, you need to first know the DRI value of protein.
The Dietary Reference value or DRI will give you a glimpse of how much protein in grams per day you should eat to stay healthy and meet your basic daily body requirements. It will serve as a base number for your daily protein intake if you are an average person with a sedentary lifestyle. The DRI value is the least amount of protein you should eat to prevent deficiency and ensuring a healthy body composition.
The RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) suggests you to eat 0.8 gram of protein per kg of body weight. And, it is 0.36 grams of protein per pound of your body weight. This means that an average male adult who has a sedentary lifestyle should consume 56 grams of daily protein. And, an average female adult with a sedentary lifestyle should consume 46 grams of protein daily.
The calculation seems simple enough from here. You can simply calculate your daily protein needs from the above formulation. Then, there should remain no confusion on how much protein you eat. Everybody can easily calculate their daily protein needs this way. But wait, there is a catch here.
Understand your Daily Protein Requirement
How much protein should you eat is directly proportional to the amount of daily protein required by your body. It can be same as the recommended daily protein intake as we have mentioned above. But the whole calculation changes if you introduce any task for your body apart from being sedentary.
The above calculation holds true only for an adult person who has a sedentary lifestyle and is inactive. Do you fall in that bracket? No, then you should read further to understand your daily protein requirement. Learn how the calculation of daily protein changes, if you introduce new challenges for your body.
Your activity level impacts the daily protein needs
The protein is an important nutrient for achieving the body composition goals. You need to have protein to lose weight, gain muscle or achieve a low body fat percentage. You will not see any change in your body composition until you consume enough protein.
Protein requirements continuously vary which is based on different type of physical activities and your intensity of the activity. An active person will need more protein than the recommended daily intake of 0.8 gram per Kg of body weight [2]. If you exercise for long hours with higher intensity, your protein and energy needs increase.
How much Protein should you eat then?
The individuals who are doing resistance training to increase muscle mass should consume 1.4-1.8 grams of protein per kg of body weight. If you are an endurance athlete, you should consume 1.2-1.4 g of protein per Kg of your body weight.
There are also times when you are on a strict diet where you have cut on carbohydrates and restrict the calories. Then your energy needs increases and you can consume up to 2 grams of protein per kg of body weight to compensate your hyper caloric diet.
Reading the above figures on how much protein you should eat can intimidate you. You can debate on the adverse effects of using too much protein in your diet. After all it is about your health and you are going to eat more protein than the recommended dietary intake. So there must be some harm in it, right? Let us first address the myths of eating too much protein and try to uncover those myths on basis of scientific studies.
In the recent years, the protein rich diet has turned very popular. Most of the people today are talking about the benefits of high protein diet both for fat loss and muscle gain. But there are speculations and myths on adverse effects of eating of too much protein in your diet. Some of the common myths are
Myth 1: High Protein Diet can cause damage to Kidneys
It is a common myth that eating a high protein diet can cause adverse effects on your kidneys. But this is not true. A lot of people think that eating too much protein puts strain to your kidneys. And, your kidneys have to work hard to excrete out nitrogen waste from the body. It is true that too much protein intake can cause kidneys to work hard. But it doesn`t mean that the kidney function get affected in any way.
Getting a disruption in kidney function in healthy adults due to increased protein intake is uncertain and has no real evidence [3]. The change in the kidney function is a normal adaption mechanism of the body and it poses no adverse effect to healthy kidneys [4].
Myth 2: Eating Too much protein leads to osteoporosis
The myth of getting osteoporosis by eating too much protein is persisting from a long time. A lot of people think that having too much protein in the diet can cause acidity in the body. The increased acid production can lead to weakened bones and you can get osteoporosis. This is true in case of increased acid production but it is not the case with protein [5].
On the contrary to this myth, not consuming enough protein can lead to weak bones and poor health. You need to have high amount of protein and consume enough calcium to support your bone health [6].
Are there any side effects of eating too much protein?
Well, you may have heard that excess of anything is bad. The case of eating too much protein is no different. Eating too much protein even more than your daily protein needs can be harmful. How much protein you should be in accordance with the daily protein needs of your body. Anything more than what is required is sure to harm you.
Let us say you are training for fat loss, so you are eating 1.2 grams of protein per Kg of your body weight. This is good. What if you start eating 2 grams of protein per day per kg of your body weight for same goal? Then it is sure, you will land in wrong place and your body has to suffer bad repercussions.
There are individuals who have no idea of how much protein they should eat and run on misguided beliefs. Those individuals are at a health risk. You are also at risk if you are following a high protein diet and have severely restricted other macro nutrients. Also, it is very important to choose the right and variety of nutritious food sources to complete your daily nutrition.
Think of a high protein diet where you are consuming foods from certain animal sources only. Let us suppose you are consuming protein only from meat sources. You haven`t included any other food sources like fish, plant based protein or dairy products. Then you can surely expect problems like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, risk of getting cancer or even heart attack [7]. Some other common side effects of eating too much protein includes
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Gas and Bloating
- Nausea
- Irritability
How to know you are eating too much Protein?
You should know when you are eating too much protein in your diet. The correct way to know this is to test for nitrogen balance in your body. Nitrogen is exclusive to the macro nutrient protein and you have learnt above the importance of nitrogen for building muscle.
So, it becomes important for you to understand nitrogen balance and get benefited from consuming protein. It will also help you understand whether the protein you are eating is enough or should you eat more?
Positive Nitrogen Balance
If the nitrogen balance in your body is positive, it means your body is in anabolic state. Having an anabolic state means you are at a positive side of muscle growth. During the positive nitrogen balance, the amount of nitrogen ingested is greater than the amount of nitrogen leaving your body. This means that how much protein you are consuming is enough to serve your body needs. You need not to add more.
Negative Nitrogen Balance
If the nitrogen balance is negative, it means your body is in catabolic stage. A catabolic stage means you are at a negative side of muscle growth. This is known to be the worst stage of an individual with right body composition goals. Having this state means the amount of nitrogen ingested is less from what your body is excreting. You need to eat more protein in this case to have muscle gain.
Equilibrium Nitrogen Balance
The state of equilibrium comes when you are losing the same amount of nitrogen as you are consuming. In this state, you are neither gaining nor losing your muscle. You should increase your daily protein intake if muscle gain is your goal.
Too Much Protein is not the only case
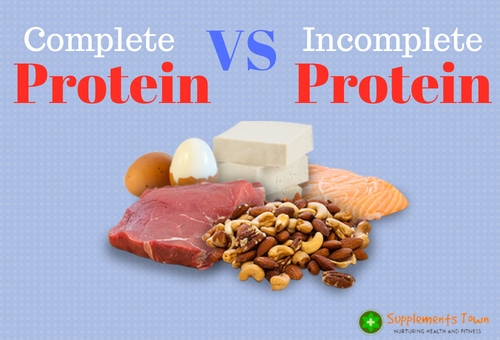
You may or may not be eating too much protein. But you will not be able to harness all the benefits of eating optimal protein until you know this. You will not get positive nitrogen balance if you are not eating complete proteins. What we mean by complete proteins is having all the 9 essential amino acids in your diet in the correct ratio.
Mainly there are two protein food sources. One is animal based protein source and another is plant based protein source. The animal sources like meat, dairy and poultry are complete proteins as they contain the essential 9 amino acids in them. On the other hand, the plant based sources except soy and quinoa are mostly incomplete sources. They don`t contain all the essential 9 amino acids.
So, you should always focus on eating variety of foods in your diet. You need not to just stick to eating one type of food for your protein needs. It is not necessary you eat the complete variety in one meal; rather you can eat different foods throughout your day. Include food sources like low fat dairy products, nuts, beans, fish, lean turkey and chicken to complete your daily protein needs.
What else should you consider with daily protein intake?
You should always consult a doctor if you are eating too much protein. Getting diagnosis for any underlying medical condition is always advisable. It will prevent any of your medical condition to get worse by eating too much protein.You should spread your daily protein intake throughout the day. Always eat a well balanced diet which contains all the macro nutrients, vegetables and fibers. You can complete your daily protein intake easily by eating 30 grams of protein per meal in your day.
Also, if you are not able to complete your protein needs from the natural sources, you can always consider taking a protein supplement. They can help you hit your daily protein target with ease. The protein supplements like whey protein, casein protein or a blend protein can be a good option to complete your daily protein needs. But, keep this mind that there is no substitute of having a well structured diet.
A quick recap
Protein is an essential macro nutrient for all your body composition goals and sound health of your body. Your daily protein needs varies and depends upon the current activity level. How much protein you can eat depends upon the DRI value of protein. But the daily protein needs increase if you have an active lifestyle.
You can eat as much protein as you want depending upon your goals and body needs. Provided, you are not experiencing any side effects or discomfort with eating too much protein. If you aren`t sure you are eating too much or too less, you can always take a nitrogen balance test.
Also, you should consume protein from different sources to take the maximum benefits from a protein rich diet. Always spread your daily protein intake among different meals and go for complete proteins in your diet.
Bibliography
- R. Y. S. Borgonha, “Nitrogen and Amino Acid Requirements,” The Massachusetts Institute of Technology Amino Acid Requirement Pattern
- PW, “Do athletes need more dietary protein and amino acids?”
- L. J. A. M. M. C. A. A. P. M. M. E. R. M. I. M. P. Stephen P. Juraschek, “Effect of a High-Protein Diet on Kidney Function in Healthy Adults”
- E. A. N. R. R. William F Martin, “Dietary protein intake and renal function”
- A. I. K. Kerstetter JE, “Dietary protein and skeletal health: a review of recent human research”
- Davis, “Could Eating Too Much Protein Increase Your Risk of Stress Fractures?”
- G. Walton, “High-Protein Diets May Slightly Increase The Risk Of Heart Disease”






That’s really a long and informative guide on protein! I appreciate your efforts you have covered all the necessary sub topics to clear the confusion!
A nice write up:)
Srishti, glad, you find the article helpful 🙂